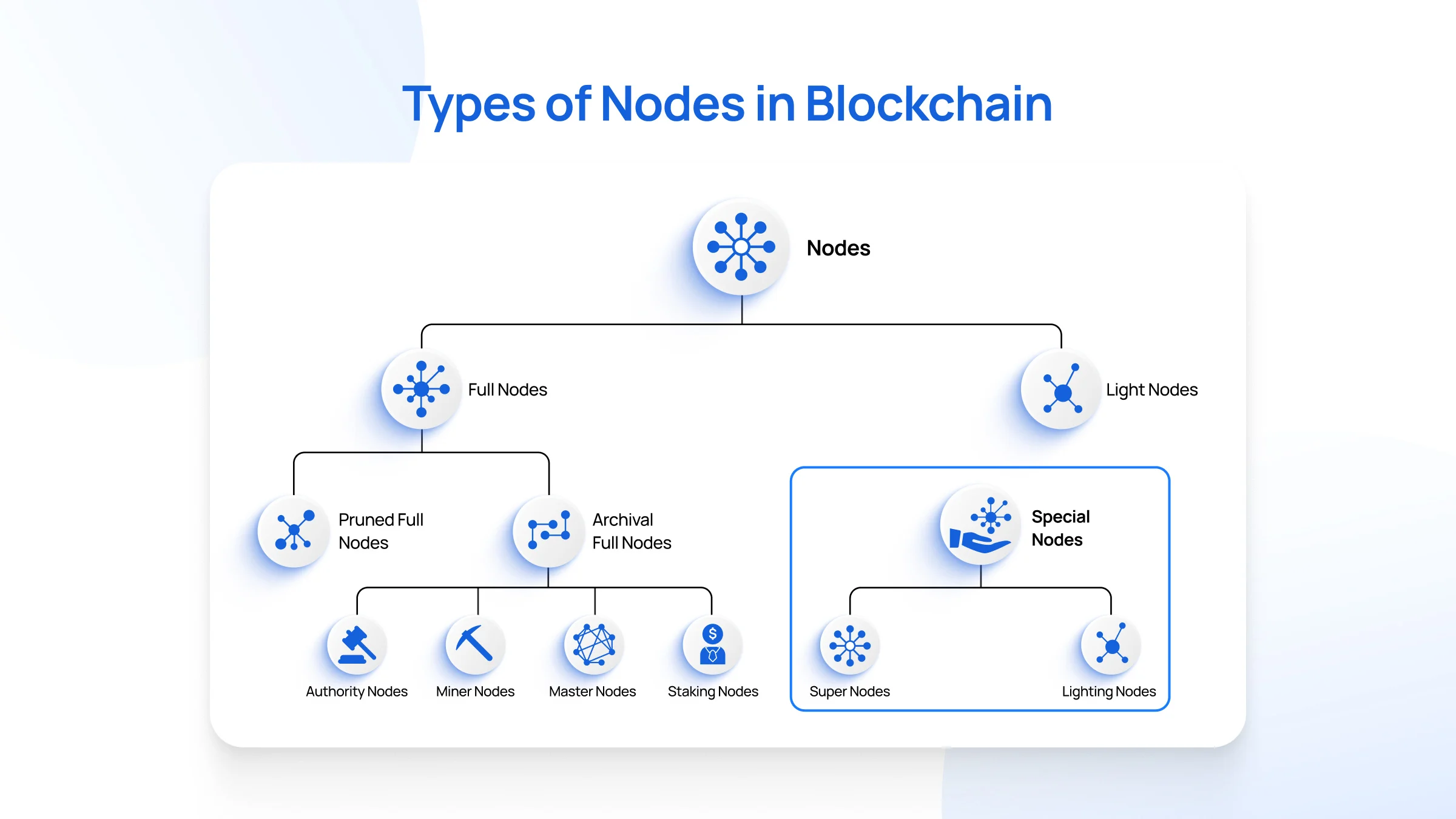
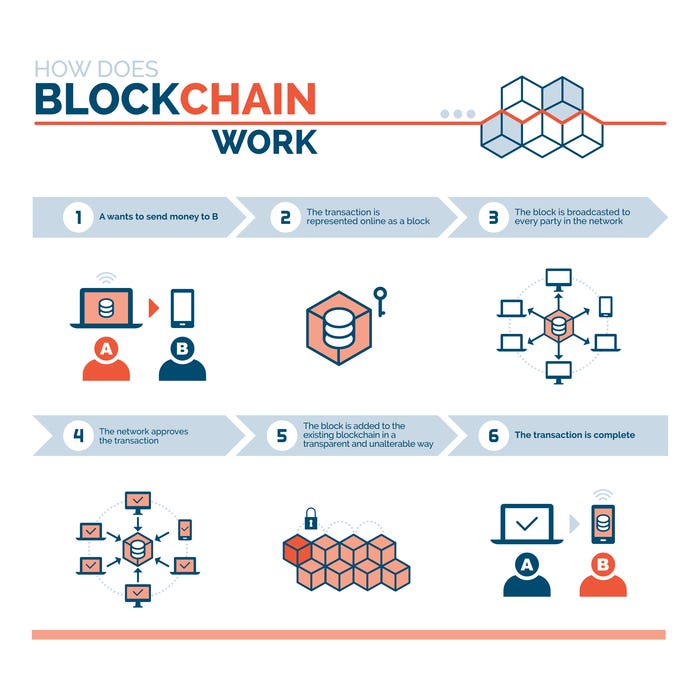
🌐 Cosmos IBC: Complete Guide to Inter-Blockchain Communication
In the constantly evolving landscape of blockchain technology, interoperability has become one of the most crucial challenges to solve. As the number of blockchains grows, so does the need for them to communicate and interact with each other seamlessly. Cosmos, often referred to as the “Internet of Blockchains,” has developed a unique and powerful solution to this issue: the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol.
This article explores Cosmos IBC in detail, including what it is, how it works, why it matters, and its implications for the broader blockchain ecosystem.
🔍 What Is Cosmos IBC?
The Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol is a core component of the Cosmos ecosystem, allowing independent blockchains to exchange data and tokens in a trustless and decentralized manner. It is part of Cosmos’ larger mission to create an ecosystem of sovereign, scalable, and interoperable blockchains.
IBC enables heterogeneous blockchains—each with their own consensus algorithm, architecture, and governance model—to interact as if they were part of a larger, interconnected network.
Think of IBC as the “TCP/IP” for blockchains. Just like how the internet connects different computer systems, IBC connects different blockchains.
🧠 Why Is Interoperability Important?
Before diving into the technicals of IBC, let’s briefly look at why interoperability matters:
- Siloed networks: Most blockchains (Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc.) operate in isolation and cannot natively interact with other chains.
- Limited composability: Without interoperability, developers can’t build cross-chain applications that utilize multiple chains’ features.
- User experience: Users must often use bridges, custodians, or centralized exchanges to move assets, which introduces friction and risk.
- Scalability: Interoperable chains can offload workloads and coordinate transactions for better throughput.
IBC solves all these by allowing trustless asset transfer, data sharing, and cross-chain smart contract interactions.
🏗️ How Cosmos IBC Works
1. Cosmos SDK and Tendermint
To understand IBC, it’s important to know that most blockchains in the Cosmos ecosystem are built using the Cosmos SDK, a modular framework for building secure, customizable blockchains.
These chains typically use Tendermint, a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus engine that ensures fast finality—crucial for IBC to work properly.
2. IBC Protocol Stack
IBC is a layered protocol, similar to how the internet has layers (like HTTP, TCP, IP).
🔸 Transport Layer (TAO)
- Responsible for authentication, ordering, and data transport between chains.
- Uses light client proofs to verify the state of another chain without needing full node trust.
🔸 Application Layer
- Handles specific use cases, such as token transfers (IBC-Transfer), staking derivatives, NFTs, etc.
🔗 How Blockchains Connect Using IBC
The IBC connection process involves three key components:
1. Clients
- Each blockchain maintains a light client of the other.
- The client is updated periodically and verifies the state of the connected chain.
2. Connections
- A secure channel is established between two chains.
- Ensures messages are delivered in the correct order and not duplicated.
3. Channels
- Each application (e.g., a token transfer module) uses a channel to send/receive data.
- Channels are bound to a specific application and use the connection layer underneath.
✉️ Message Flow Example (IBC Token Transfer)
- User on Chain A initiates a transfer to Chain B.
- The token is locked on Chain A.
- A message is sent over IBC to Chain B.
- Chain B receives the message and mints a voucher token representing the locked asset.
- When the user returns the token, Chain B burns it, and Chain A unlocks the original.
This trustless flow ensures that no central authority is needed to move tokens between chains.
⚙️ IBC Modules and Standards
IBC is designed to be modular and extensible. Some common IBC modules include:
- IBC-Transfer: The most widely used, for transferring fungible tokens.
- ICS (IBC Specification): Standardized components of the IBC protocol.
- ICS-20: Token transfers.
- ICS-721: NFT transfers.
- ICS-27: Cross-chain smart contract calls (interchain accounts).
With more ICS modules in development, IBC is set to enable even more complex forms of interoperability.
🔥 Real-World Examples of IBC in Action
1. Osmosis
A leading DeFi platform in Cosmos, Osmosis uses IBC to allow users to swap tokens from multiple chains (e.g., ATOM, JUNO, STARS) without using a centralized exchange.
2. Juno
An interoperable smart contract platform that leverages IBC to expand its user base and functionality.
3. Stargaze
An NFT platform connected via IBC, enabling users to transfer NFTs between blockchains.
4. Gravity Bridge
A bridge between Ethereum and Cosmos that uses IBC to facilitate asset transfers.
🛡️ Security and Challenges
✅ Strengths
- No trusted intermediaries.
- Fast finality with Tendermint improves trustless messaging.
- Extensible for multiple use cases.
⚠️ Challenges
- Limited to BFT-based chains: IBC requires fast finality, so it doesn’t work natively with proof-of-work chains (like Bitcoin).
- IBC Relayers: These are required to transmit packets and must be incentivized.
- Complex UX: While powerful, the complexity can be high for end users unfamiliar with cross-chain logic.
🚀 The Future of Cosmos IBC
IBC continues to evolve rapidly. Some key developments ahead include:
1. IBC Expansion Beyond Cosmos
While IBC is native to Cosmos SDK chains, efforts like CometBFT and IBC-go are bringing it to other blockchain platforms like:
- Ethereum (via rollups and bridges),
- Polkadot (via parachain integrations),
- Avalanche and more.
2. Interchain Security
A major upgrade that allows chains to share validators from the Cosmos Hub, improving security and lowering costs.
3. Interchain Accounts
Enables one blockchain to control an account on another chain, allowing for cross-chain smart contracts and DeFi operations.
4. IBC V2 and Mesh Networking
Future versions will support multi-hop routing (A → B → C) and reduce latency and costs even further.
💡 Conclusion
Cosmos IBC represents a major step forward in the evolution of decentralized, interoperable blockchain networks. By enabling secure and efficient cross-chain communication, IBC opens the door to a future where blockchains are not isolated silos but interconnected systems working in harmony.
Whether it’s for token transfers, data exchange, or building complex DeFi ecosystems across multiple chains, IBC is at the heart of the modular and scalable multichain future.
As adoption continues and more chains integrate IBC, the Cosmos vision of an Internet of Blockchains is quickly becoming a reality.