Futures vs Options in Crypto: A Comprehensive Guide
Cryptocurrency trading has evolved significantly in recent years, with more complex instruments becoming available to traders seeking to maximize their returns. Among the most popular derivatives in crypto trading are futures and options. These instruments allow traders to speculate on the future price movements of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, without actually owning the assets. While both futures and options can be highly profitable, they come with distinct characteristics and risks. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between futures and options in the cryptocurrency market, their advantages, disadvantages, and how traders can use them to enhance their strategies.
What Are Futures in Crypto?
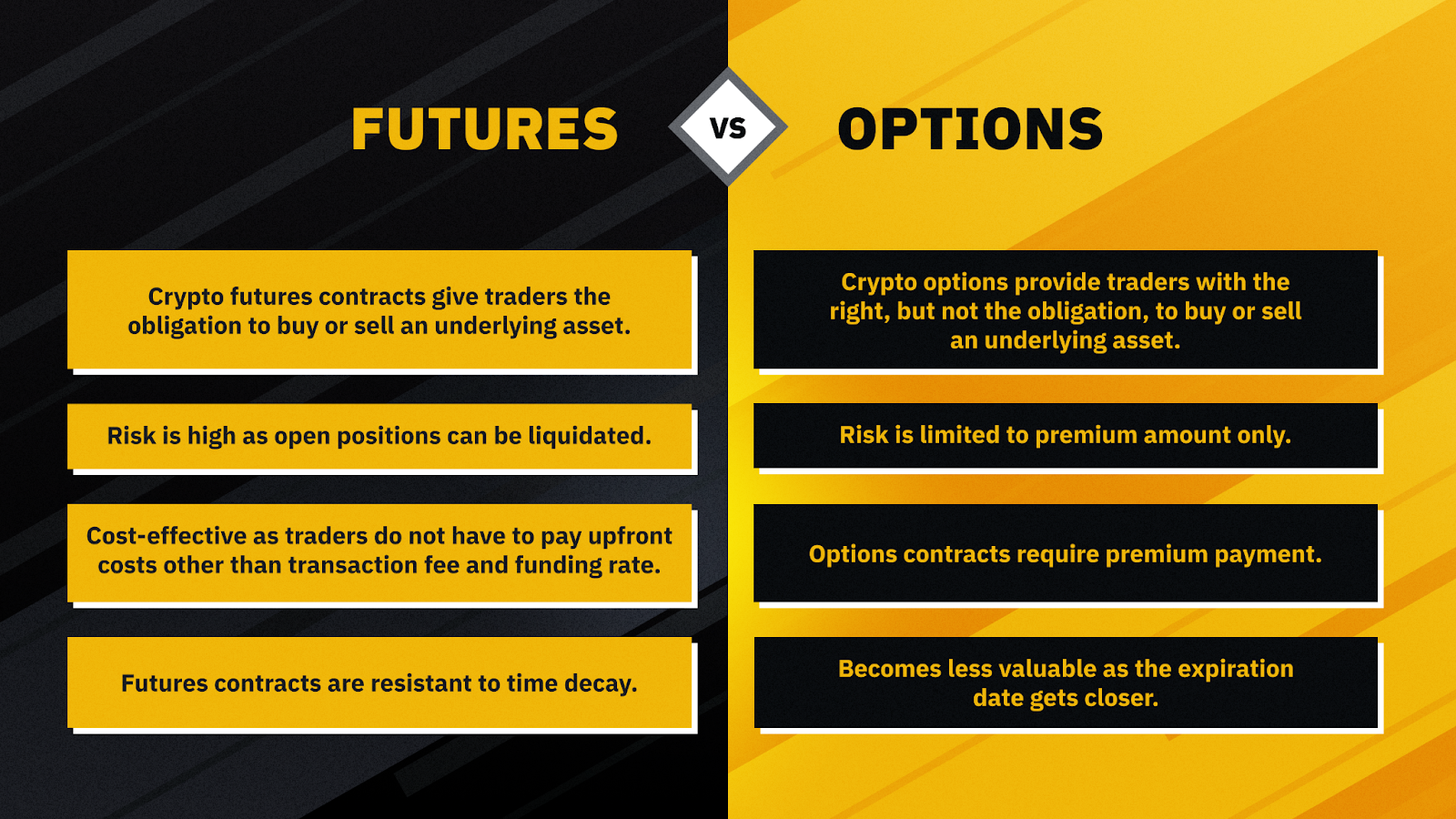
Futures contracts are standardized agreements between two parties to buy or sell a cryptocurrency at a predetermined price on a specified future date. Essentially, a futures contract locks in a price at which the buyer and seller agree to transact at the contract’s expiration.
Futures in crypto work similarly to traditional financial markets, where traders can take both long (buy) or short (sell) positions, depending on whether they believe the price of a crypto asset will rise or fall.
Key Features of Crypto Futures:
- Leverage: One of the most attractive aspects of crypto futures is the ability to trade with leverage. Leverage allows traders to control a larger position than they could with just their own capital. For example, with 10x leverage, a trader can control $10,000 worth of crypto with just $1,000 in margin.
- Expiration Date: Futures contracts have an expiration date, meaning they must be settled (either through cash settlement or delivery of the underlying asset) by a specific date. This creates time constraints for traders to make their predictions profitable.
- Obligation: In futures contracts, both parties are obligated to honor the agreement at the expiration date, whether the market moves in their favor or not. This can result in significant losses if the market moves unfavorably.
- Hedging: Futures are often used by institutional investors or traders to hedge against price volatility. For instance, a crypto exchange might use futures contracts to protect themselves against significant market fluctuations.
Advantages of Crypto Futures:
- Profit from Both Rising and Falling Markets: Traders can take long (buy) or short (sell) positions, making it possible to profit in both bull and bear markets.
- Leverage: Crypto futures allow traders to amplify their potential profits, making it a highly attractive option for experienced traders.
- Liquidity: Many popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have highly liquid futures markets, allowing for easy entry and exit.
Disadvantages of Crypto Futures:
- High Risk: While leverage can magnify profits, it can also lead to massive losses, especially in volatile markets.
- Expiration Risk: Futures contracts expire on a specific date, so traders have to make accurate predictions within a limited time frame, or they risk losing their investment.
- Complexity: Futures are generally more complex than spot trading, and their proper use requires a good understanding of the market and risk management.
What Are Options in Crypto?
Options contracts, on the other hand, provide the holder with the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified period. In the case of cryptocurrencies, options work similarly to traditional stock options but are based on digital currencies like Bitcoin.
There are two primary types of options:
- Call Options: A call option gives the buyer the right to buy a cryptocurrency at a specific price (called the strike price) before the option expires.
- Put Options: A put option gives the buyer the right to sell a cryptocurrency at a specific price before the option expires.
In crypto options, traders can also take either long (buy) or short (sell) positions. However, unlike futures, the buyer of an options contract is not obligated to execute the trade. The seller, on the other hand, is obligated to fulfill the contract if the buyer decides to exercise the option.
Key Features of Crypto Options:
- Premium: The buyer of an options contract must pay a premium upfront to acquire the option. This premium is the maximum amount the buyer can lose if the market moves unfavorably.
- Expiration: Like futures, options contracts also have expiration dates. If the option is not exercised before this date, it expires worthless.
- No Obligation: One of the key differences between options and futures is that options give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to exercise the contract. This makes options less risky for buyers compared to futures.
- Flexibility: Options provide more flexibility compared to futures. A trader can choose to exercise the option, sell it to another trader, or let it expire.
Advantages of Crypto Options:
- Limited Risk for Buyers: The most significant advantage of options is that the buyer’s risk is limited to the premium paid for the option. This makes options a potentially safer choice for traders looking to speculate on market movements.
- Strategic Flexibility: Options provide traders with more strategies, such as writing covered calls or using spreads, which can reduce risk and enhance returns.
- Leverage: Like futures, options allow traders to leverage their position, as they only need to pay the premium rather than the full value of the underlying asset.
Disadvantages of Crypto Options:
- Premium Cost: The upfront cost of purchasing an options contract (the premium) can be high, especially for highly volatile assets like Bitcoin.
- Complexity: Options are often more complex than futures and can be challenging for beginners to understand and trade effectively.
- Time Decay: Options lose value over time, particularly as they approach their expiration date, which means that even if the market moves in the desired direction, a trader might not profit if too much time passes.
Key Differences Between Futures and Options
1. Obligation vs. Right
The most significant difference between futures and options is the nature of the contract. In a futures contract, both parties are obligated to execute the contract at the agreed-upon price on the expiration date. In contrast, options give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to execute the contract.
2. Risk and Reward
- Futures: The risk is theoretically unlimited, especially when trading with leverage. If the market moves significantly against a trader’s position, they could lose more than their initial margin.
- Options: The risk for the buyer is limited to the premium paid, meaning that the potential loss is fixed. However, options sellers face potentially unlimited risk if the market moves significantly against them.
3. Complexity
Both futures and options require a good understanding of the underlying asset and the market conditions. However, options tend to be more complex due to the various strategies that can be used and the time decay factor.
4. Leverage
Both instruments offer leverage, but futures tend to offer more leverage compared to options. This makes futures attractive to traders seeking high-risk, high-reward opportunities.
Conclusion
Both futures and options are powerful tools for crypto traders, offering unique advantages and strategies for profiting from the volatility of digital assets. Futures contracts are well-suited for those who want to make large leveraged bets on the direction of the market, while options are more flexible and provide limited risk for buyers. However, both come with their own set of risks, including the potential for significant losses, especially when using leverage.
Traders should carefully evaluate their risk tolerance, trading strategy, and market conditions before deciding to use either of these instruments. For beginners, starting with simpler trading methods and gradually learning the ins and outs of futures and options trading is essential to minimize risk and optimize profits in the crypto space.