Smart Contracts 101: Everything You Need to Know
In the rapidly evolving world of blockchain and cryptocurrency, smart contracts stand out as one of the most groundbreaking innovations. These self-executing agreements have the potential to reshape how we conduct transactions, manage agreements, and automate processes across industries — all without the need for middlemen.
In this article, we’ll break down what smart contracts are, how they work, their benefits and risks, and how they’re changing industries from finance to healthcare and beyond.
🔍 What Is a Smart Contract?
A smart contract is a self-executing computer program that automatically enforces the terms of an agreement written into its code. It runs on a blockchain, which ensures transparency, immutability, and security.
Unlike traditional contracts — which require intermediaries like lawyers, brokers, or notaries to validate or enforce terms — smart contracts operate without human intervention once deployed.
Key Characteristics:
- Autonomous: Once initiated, no need for third-party involvement.
- Deterministic: Same input always produces the same result.
- Immutable: Cannot be changed once deployed on the blockchain.
- Transparent: Code and transactions are visible on public blockchains.
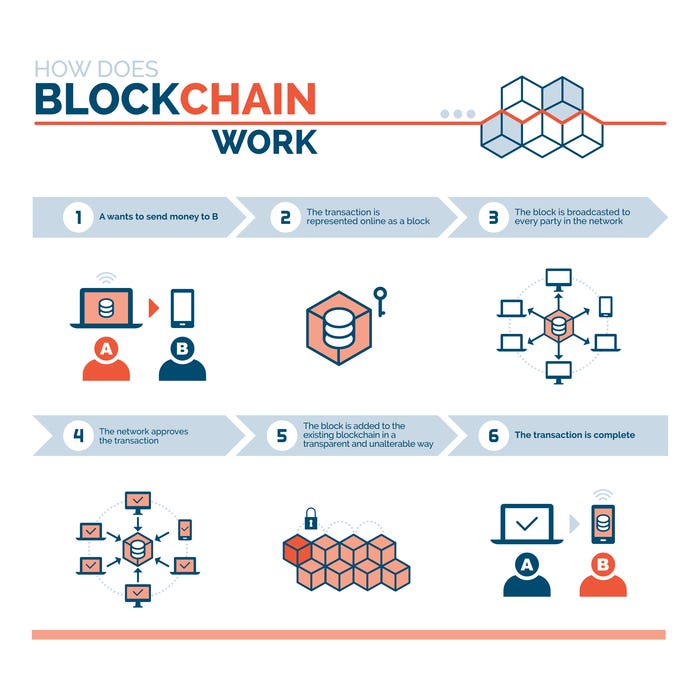
⚙️ How Do Smart Contracts Work?
Smart contracts are typically deployed on blockchain platforms that support programming logic — most notably Ethereum. They’re written in programming languages like Solidity (for Ethereum) or Rust (for Solana).
Here’s how it works in a simple scenario:
- Two parties agree on terms (e.g., a buyer and a seller).
- A smart contract is coded with those terms and deployed to the blockchain.
- When the conditions are met (e.g., goods delivered), the contract automatically executes (e.g., payment is released).
- The transaction is recorded on the blockchain — secure, transparent, and irreversible.
Example:
Alice wants to buy a digital artwork from Bob. They use a smart contract that releases payment to Bob only when Alice receives the file. The contract ensures both parties uphold their end of the deal — without any trust or a third-party platform.
✅ Benefits of Smart Contracts
1. Trustless Execution
No need to trust the other party — the contract enforces itself based on code.
2. Cost-Efficient
Eliminates fees paid to lawyers, brokers, or intermediaries.
3. Speed
Automates processes that would otherwise take hours or days.
4. Transparency
All contract actions are visible on the blockchain.
5. Security
Immutable code and encryption make tampering nearly impossible.
6. Global Access
Anyone with internet and crypto wallet access can interact with smart contracts.
❗ Risks and Limitations
While smart contracts are revolutionary, they’re not without challenges:
1. Code Bugs
Poorly written code can lead to exploits — such as the infamous DAO hack in 2016, which led to a loss of millions in Ether.
2. Lack of Legal Recognition
In many countries, smart contracts aren’t yet legally enforceable.
3. Irreversibility
Once deployed, they cannot be altered — a double-edged sword if there’s a mistake.
4. Complexity
Creating reliable contracts requires specialized knowledge in both programming and law.
🔐 Real-World Use Cases of Smart Contracts
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Smart contracts power DeFi platforms like Uniswap, Compound, and Aave, enabling borrowing, lending, and trading of crypto assets without banks.
2. NFT Marketplaces
Smart contracts ensure ownership transfer and royalty payments on platforms like OpenSea and Rarible.
3. Insurance
Contracts can automatically pay out when conditions are met — for example, travel insurance that pays if a flight is canceled.
4. Supply Chain
Track goods from origin to destination. Smart contracts trigger payments when goods reach checkpoints.
5. Gaming
Blockchain-based games use smart contracts to mint and transfer digital assets securely and transparently.
6. Real Estate
Enables tokenized property sales where ownership transfers via blockchain once payments are confirmed.
🧱 Platforms That Support Smart Contracts
🔹 Ethereum
The pioneer and most widely used smart contract platform, supporting thousands of decentralized applications (dApps).
🔹 Binance Smart Chain (BSC)
A cheaper, faster alternative to Ethereum, compatible with Ethereum’s tools.
🔹 Solana
Known for high-speed and low-cost smart contracts, especially in gaming and NFTs.
🔹 Cardano
Focuses on research-driven development and secure smart contract deployment.
🔹 Polkadot and Avalanche
Provide scalable, interoperable environments for cross-chain smart contracts.
📘 Programming Languages for Smart Contracts
- Solidity: Primary language for Ethereum.
- Vyper: Python-like language for Ethereum with simpler syntax.
- Rust: Used by Solana, NEAR, and others.
- Move: Developed by Meta (formerly Facebook), used in Aptos and Sui.
⚖️ Legal and Regulatory Outlook
Smart contracts exist in a grey legal area in many jurisdictions. Some regions like Arizona and Tennessee in the U.S. have begun recognizing smart contracts in their legal frameworks. Still, widespread adoption will require:
- Standardization of smart contract language;
- Legal clarity about enforceability;
- Integration with traditional legal processes.
🧠 Future of Smart Contracts
As blockchain adoption grows, smart contracts will become more user-friendly, secure, and integrated with AI and IoT. Some upcoming trends include:
- Oracles: Services like Chainlink that bring off-chain data (weather, price feeds) into smart contracts.
- Layer 2 solutions: Like Arbitrum and Optimism, helping scale Ethereum smart contracts with lower fees.
- Cross-chain contracts: Enabling interaction between different blockchains.
📝 Conclusion
Smart contracts are revolutionizing how agreements and transactions are executed. By removing intermediaries, enhancing trust, reducing cost, and improving transparency, they’re paving the way for a decentralized future.
While challenges like legal recognition and technical complexity remain, the potential is enormous. Whether you’re a developer, investor, or simply curious about crypto, understanding smart contracts is key to navigating the blockchain ecosystem.