🧠 Understanding Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain: Full Guide
In the realm of blockchain technology, consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in maintaining security, trust, and decentralization. Without a central authority, blockchains rely on consensus protocols to validate transactions, confirm blocks, and ensure every participant agrees on the state of the network.
Whether you’re a crypto enthusiast, developer, or investor, understanding how consensus works is key to navigating the blockchain space. Let’s dive into the full details of what consensus mechanisms are, why they matter, and the different types used today.
📌 What is a Consensus Mechanism?
A consensus mechanism is a protocol used by blockchain networks to achieve agreement among distributed participants (called nodes) on the validity of data — especially transactions and the current state of the ledger.
In simpler terms, it ensures that everyone on the network agrees on what is true, without relying on a central authority.
Why Is It Necessary?
Blockchain is decentralized — there’s no one server or administrator to decide which transactions are valid. Therefore, participants must collectively agree on:
- Which transactions to add to the ledger
- Which blocks are valid
- The order of transactions
- How to prevent double spending or fraud
This is made possible through consensus algorithms.
🏗️ Key Functions of Consensus Mechanisms
- Validation of Transactions
- Only legitimate transactions are recorded on the blockchain.
- Agreement on a Single Version of Truth
- Prevents forks or conflicting versions of the ledger.
- Securing the Network
- Makes it extremely difficult for bad actors to manipulate the system.
- Ensuring Fair Participation
- Offers equal opportunities for nodes to contribute (depending on the algorithm used).
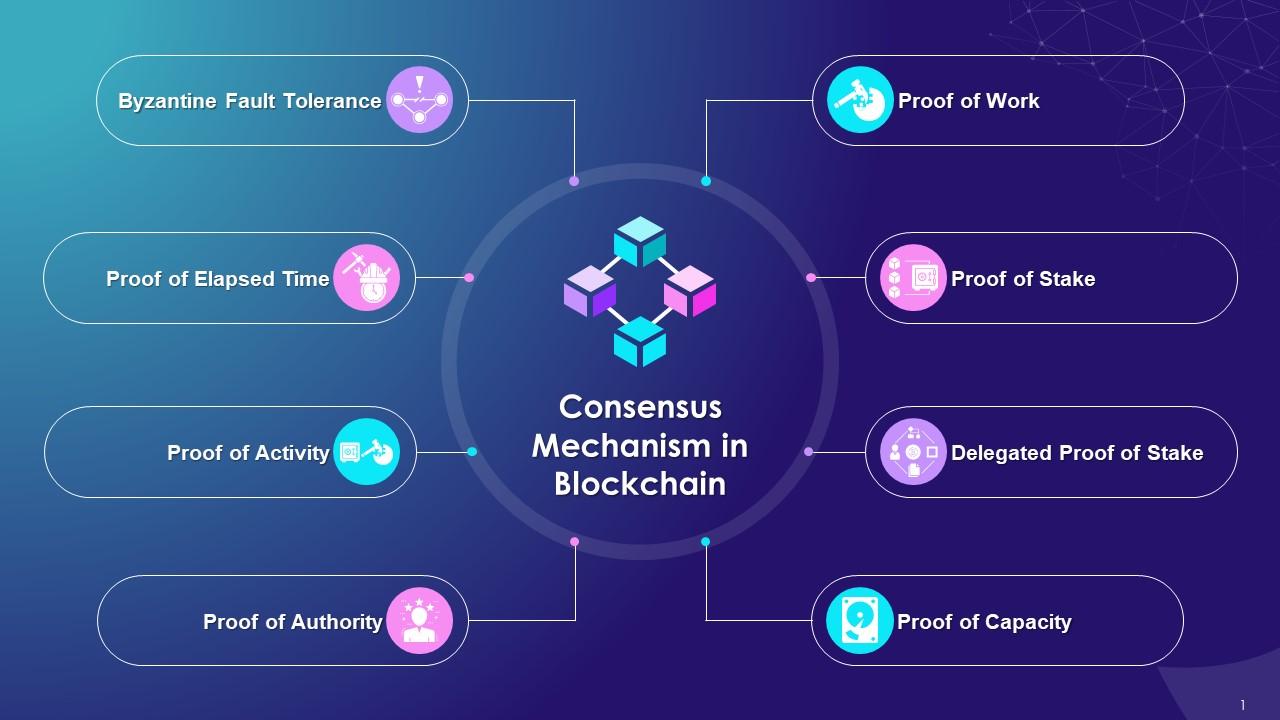
🔐 Popular Types of Consensus Mechanisms
Let’s explore the most common and influential consensus mechanisms used in the blockchain ecosystem.
1. Proof of Work (PoW)
Used By: Bitcoin, Litecoin, Dogecoin (and previously Ethereum)
How It Works:
Miners solve complex cryptographic puzzles using computing power. The first to solve it earns the right to add a new block and is rewarded with cryptocurrency.
Pros:
- Highly secure and time-tested
- Resistant to Sybil attacks (fake nodes)
Cons:
- High energy consumption
- Expensive hardware requirements
- Slower transaction throughput
2. Proof of Stake (PoS)
Used By: Ethereum (since The Merge), Cardano, Polkadot, Tezos
How It Works:
Participants “stake” their cryptocurrency as a guarantee. Validators are randomly selected to create new blocks and validate transactions based on the size and duration of their stake.
Pros:
- Energy efficient
- Lower hardware requirements
- Encourages long-term network investment
Cons:
- Wealthy participants may have more influence
- Still evolving in terms of security compared to PoW
3. Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
Used By: EOS, Tron, BitShares
How It Works:
Token holders vote for a limited number of delegates who validate transactions and produce blocks. These delegates are held accountable by the voters.
Pros:
- High scalability and fast transactions
- Community-driven governance
Cons:
- Less decentralized than PoW/PoS
- Risk of centralization in voting power
4. Proof of Authority (PoA)
Used By: VeChain, private blockchains like Microsoft’s Azure Blockchain
How It Works:
A few pre-approved and reputable validators (authorities) validate transactions. Their identity is public and reputation-based.
Pros:
- Very fast and efficient
- Ideal for private or consortium blockchains
Cons:
- Centralized — not ideal for public, trustless systems
- Susceptible to collusion
5. Proof of Space (also known as Proof of Capacity)
Used By: Chia
How It Works:
Instead of computing power, users dedicate hard drive space to “plot” data. The more space you provide, the higher the chance of winning the block.
Pros:
- Less energy-intensive than PoW
- Makes use of available storage
Cons:
- Requires significant disk space
- Can reduce SSD lifespan
6. Proof of Burn (PoB)
How It Works:
Users “burn” (permanently destroy) coins by sending them to an unusable address. This sacrifice proves commitment, and they gain the right to validate blocks.
Pros:
- Deters bad actors
- Reduces token supply (deflationary effect)
Cons:
- Wasteful in terms of capital
- Low adoption rate
7. Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET)
Used By: Hyperledger Sawtooth
How It Works:
Nodes wait for a random amount of time before being allowed to propose a block. The node with the shortest wait wins.
Pros:
- Fair and efficient
- Low energy usage
Cons:
- Requires a trusted execution environment (e.g., Intel SGX)
- Not fully decentralized
🧠 Comparing Consensus Mechanisms
| Mechanism | Speed | Energy Use | Decentralization | Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PoW | Slow | High | High | Mature |
| PoS | Fast | Low | High | Growing |
| DPoS | Very Fast | Low | Medium | Moderate |
| PoA | Very Fast | Very Low | Low | Used in private chains |
| PoSpace | Medium | Low | Medium | Niche use |
| PoB | Slow | Medium | High | Rare |
🌍 Why Consensus Mechanisms Matter for Blockchain Projects
When launching or investing in a blockchain-based project, the consensus mechanism can affect:
- Security: A weaker mechanism is more vulnerable to attacks.
- Scalability: Faster mechanisms can handle more users.
- Governance: Some allow more community control, others are centralized.
- Energy efficiency: Especially important in environmentally conscious ecosystems.
- Cost: PoW often involves higher transaction fees than PoS or DPoS.
🔮 The Future of Consensus
As blockchain technology evolves, hybrid and novel consensus algorithms are being developed:
- Hybrid PoW + PoS (used by Decred) combines the security of PoW with the energy efficiency of PoS.
- Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) — used in IOTA and Nano — are moving away from traditional blocks altogether.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Rollups are being integrated with consensus to boost privacy and scalability (especially in Layer 2 solutions).
Blockchain networks will continue to innovate to meet the demands of speed, security, and decentralization.
✅ Conclusion
Consensus mechanisms are the heartbeat of blockchain networks. They enable trustless environments where people across the globe can exchange value and data without intermediaries.
Understanding the different types of consensus algorithms — from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake and beyond — gives you insight into how blockchain networks function, scale, and evolve.
Whether you’re building on blockchain, investing in cryptocurrencies, or just learning, consensus is a foundational concept that shapes the entire crypto ecosystem.