How Leverage Works in Forex Trading: A Complete Guide
Leverage in Forex trading is one of the most powerful tools available to traders, allowing them to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. However, with this power comes greater risk. Understanding how leverage works and how to use it responsibly is essential for anyone entering the world of Forex trading. In this article, we will explain leverage in Forex trading in detail, including how it works, the risks involved, and how traders can manage it effectively.
What Is Leverage in Forex Trading?
Leverage is the ability to control a large position in the market with a smaller amount of capital. In Forex trading, leverage allows traders to amplify their potential returns by borrowing funds from their broker. For example, if a trader uses leverage of 50:1, they can control $50,000 worth of currency with just $1,000 of their own capital.
In simple terms, leverage means that a trader can enter into a position much larger than the amount of money they actually have in their trading account. It’s like borrowing money to increase the size of your trades.
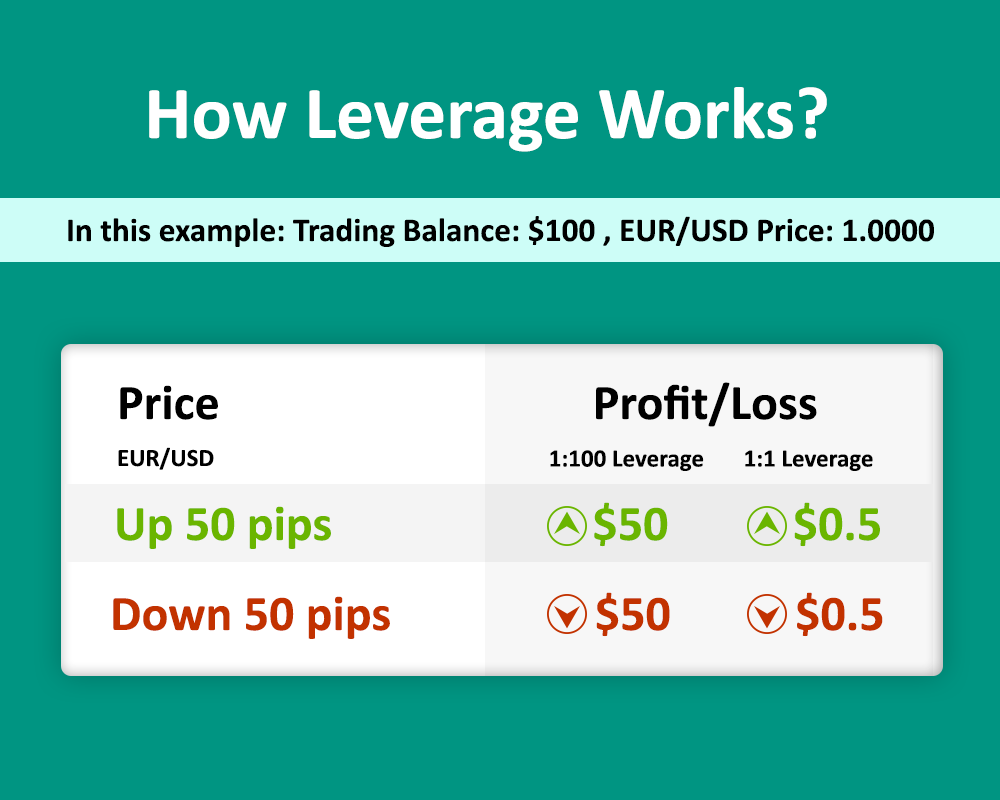
How Does Leverage Work in Forex?
Let’s break it down further with a simple example:
- Suppose a trader has $1,000 in their account and they use leverage of 50:1. This means they can control a position worth $50,000 (50 x $1,000).
- If the price of the currency pair moves in their favor by 1%, they make a profit of $500 (1% of $50,000), which is 50% of their initial $1,000 investment.
- Conversely, if the price moves against them by 1%, they would incur a loss of $500, which is 50% of their initial investment.
Thus, leverage magnifies both potential profits and potential losses. It can lead to significant gains when the market moves in the trader’s favor but also carries the risk of significant losses when the market moves against the trader.
Common Leverage Ratios in Forex Trading
Leverage ratios vary across brokers and markets. Forex brokers typically offer leverage ranging from 10:1 to 1000:1, depending on the trader’s account type, the currency pair, and the country’s regulations.
Here are some common leverage ratios and their implications:
- 50:1 Leverage: For every $1 in your account, you can control $50 in the market. This is a moderate level of leverage that provides a balance between risk and reward.
- 100:1 Leverage: For every $1 in your account, you can control $100. This offers a higher level of risk and reward.
- 500:1 Leverage: For every $1 in your account, you can control $500. This is high leverage and can lead to substantial profits or losses.
- 1000:1 Leverage: For every $1 in your account, you can control $1,000. This level of leverage is extremely high and is considered risky for most traders, especially those without a deep understanding of risk management.
Margin and Leverage
Margin is the amount of money required in your trading account to open a leveraged position. It is essentially the “good faith deposit” you provide to the broker to take on a larger position than your account balance would otherwise allow.
For example:
- If you want to trade a position worth $50,000 with leverage of 50:1, the margin required would be 1/50th of $50,000, which is $1,000.
- The margin is essentially the amount of money the broker requires to “borrow” to allow you to control a larger position.
Leverage and margin go hand in hand. The higher the leverage you use, the less margin you need in your account to open a position. However, this also means that small market movements can have a bigger impact on your margin.
The Risks of Leverage in Forex Trading
While leverage can amplify profits, it also comes with significant risks. The most important risk of leverage is that it can lead to substantial losses. Traders can lose more money than they initially invested if the market moves against them.
Here are some of the key risks involved with using leverage in Forex:
- Magnified Losses: Just as leverage can increase profits, it can also magnify losses. In the example above, a 1% adverse move in the market could result in a 50% loss of the trader’s initial capital when using leverage of 50:1.
- Margin Call: If the losses in your account exceed a certain threshold, your broker may issue a margin call. This means you will need to deposit more funds to maintain your position, or your position will be automatically closed at a loss.
- Overtrading: The ability to control large positions with a small amount of capital can lead to overtrading, where traders take excessive risks, believing that the small margin required to control large positions minimizes the risk. Overtrading can quickly lead to significant losses.
- Volatility Risk: Forex markets can be highly volatile, and using leverage increases exposure to these price fluctuations. Even small price movements can lead to large profits or substantial losses.
- Psychological Pressure: The pressure of potentially losing a significant portion of your capital can lead to poor decision-making. Emotional trading is often amplified under the effects of high leverage, leading to impulsive actions that can result in larger losses.
How to Manage Leverage Effectively
While leverage can be a useful tool, it’s essential to use it wisely. Here are some tips to help you manage leverage in Forex trading effectively:
- Start Small: If you’re new to Forex trading, start with low leverage. A good starting point is 10:1 or 20:1 leverage. This will allow you to get familiar with market dynamics without risking too much capital.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: A stop-loss order is an order placed with a broker to automatically close a trade if it reaches a certain loss level. Stop-loss orders are essential for managing risk and protecting your capital.
- Don’t Overleverage: Avoid using the maximum leverage offered by your broker. While it may seem tempting, using too much leverage can lead to massive losses. Only use leverage that you are comfortable with and can afford to lose.
- Have a Solid Risk Management Plan: Develop a risk management strategy that includes risk per trade, position sizing, and setting realistic profit and loss targets. This will help you stay disciplined and prevent emotional trading.
- Understand Margin Calls: Be aware of the margin requirements and always monitor your account closely. Ensure that you have enough margin to avoid a margin call.
- Regularly Review Your Trades: Continuously evaluate your trades and make adjustments as needed. Keep learning and stay updated on market conditions to make informed decisions.
Conclusion
Leverage is a powerful tool in Forex trading, but it’s not without its risks. While it offers the potential for significant profits, it also increases the likelihood of substantial losses. Traders should use leverage responsibly and only with a solid understanding of how it works and how to manage risk.
By using proper risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders, avoiding overleveraging, and starting with smaller positions, traders can take advantage of the benefits of leverage without falling victim to its dangers. Remember, in Forex trading, discipline and knowledge are the keys to success.