What is a Spread in Forex Trading? A Complete Guide
Forex trading involves the buying and selling of currencies, and like all markets, there’s a cost to participating. One of the most important yet often misunderstood concepts in Forex is the spread. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding how spreads work is critical to evaluating trading costs and planning effective strategies.
In this guide, we’ll break down what a spread is in Forex trading, the types of spreads, how they’re calculated, and why they matter.
What is a Spread in Forex Trading?
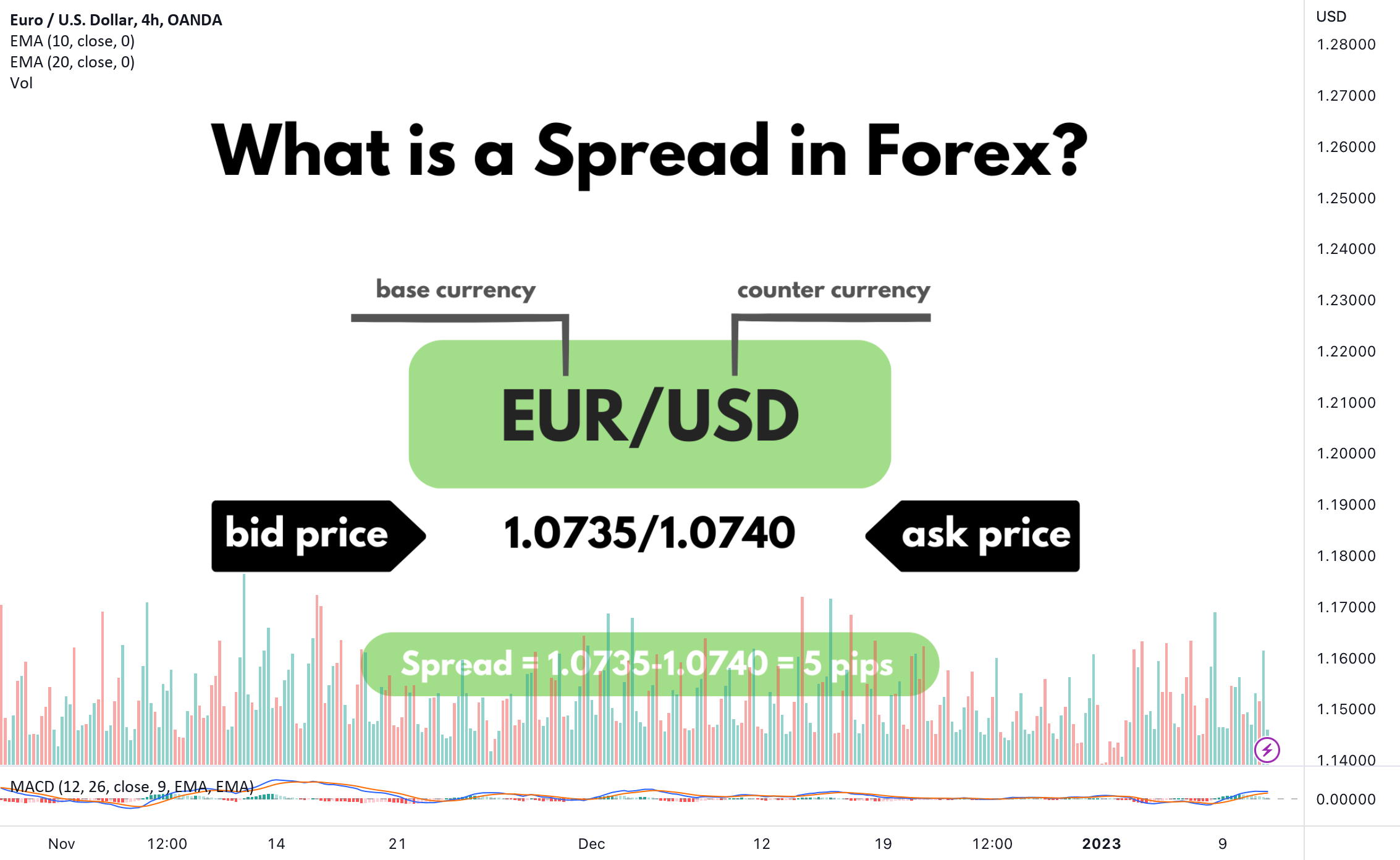
In simple terms, a spread is the difference between the bid price and the ask price of a currency pair.
- Bid price: The price at which a broker is willing to buy a currency from a trader.
- Ask price: The price at which a broker is willing to sell a currency to a trader.
The spread represents the broker’s fee or commission for facilitating the trade. Instead of charging a flat fee, many Forex brokers make money through this price difference.
How Does Spread Work?
Let’s take an example:
Suppose the EUR/USD currency pair is quoted as:
- Bid: 1.1000
- Ask: 1.1002
The spread here is:
1.1002 – 1.1000 = 0.0002 or 2 pips
This means that when you enter a trade, you’ll start with a slight loss equivalent to the spread amount. The market has to move in your favor by at least 2 pips before your trade becomes profitable.
Types of Spreads in Forex
There are two main types of spreads you’ll encounter:
1. Fixed Spread
- The difference between the bid and ask price remains constant regardless of market conditions.
- Offered by market maker brokers.
- Beneficial in volatile markets because costs are predictable.
- May have slightly higher spreads overall.
2. Variable (Floating) Spread
- The spread changes depending on market volatility and liquidity.
- Offered by ECN or STP brokers.
- Can be as low as 0.1 pips during stable times, but widen significantly during news events.
- Suitable for experienced traders who can manage risk.
What Affects the Spread in Forex?
Several factors influence the spread, including:
- Liquidity of the currency pair: Major pairs like EUR/USD have tighter spreads than exotic pairs like USD/TRY.
- Market volatility: During high-impact news events, spreads can widen dramatically.
- Broker type: Market makers often offer fixed spreads, while ECN brokers offer floating spreads.
- Time of day: Spreads are usually lower during major trading sessions (London and New York) and wider during off-hours.
Why is Spread Important in Forex Trading?
Understanding spreads is important because:
- It affects your trading costs: Higher spreads mean higher costs.
- Impacts scalping and short-term strategies: Frequent trades with tight targets can be heavily affected by even small spreads.
- Influences profitability: A large spread can eat into potential profits or deepen losses.
How to Calculate the Spread Cost
Here’s a simple formula:
Spread Cost = Spread in Pips × Pip Value × Lot Size
Example:
- Spread = 2 pips
- Pip Value = $10 (for a standard lot of 100,000 units)
- Lot Size = 1 lot
Spread Cost = 2 × $10 = $20
So, opening this position would cost $20 immediately due to the spread.
How to Reduce Spread Costs
- Trade Major Currency Pairs – These typically have the lowest spreads due to high liquidity.
- Avoid Trading During High Volatility – Spreads tend to widen around major news releases.
- Choose the Right Broker – Look for brokers with competitive spreads and transparent pricing.
- Use ECN Accounts (if experienced) – These offer lower spreads but may charge a commission.
Spread vs Commission
- Spread-based brokers: Include their fees in the spread.
- Commission-based brokers: Offer tighter spreads but charge a separate trading commission.
Depending on your strategy, one model may be more cost-effective than the other.
Tools to Monitor Spread
Most trading platforms like MetaTrader 4/5 allow traders to view real-time spreads. You can:
- Add a spread indicator on your chart
- Use the Market Watch window to check bid/ask prices
- Use a spread monitoring tool to track historical spreads over time
Conclusion
The spread in Forex trading is a small but crucial concept that can significantly impact your trading performance. Whether fixed or variable, the spread represents your upfront cost when opening a trade. By understanding how spreads work and factoring them into your trading strategy, you can make more informed decisions and better manage your trading expenses.
Before entering the market, always check the spread on your chosen currency pair, especially during volatile conditions or outside of major trading sessions.